Sulfur in Magmas
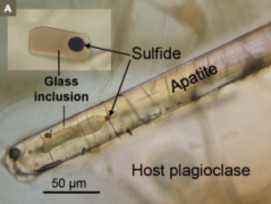
Sulfur is a ubiquitous element whose variable valence states (S2-, S0, S4+, S6+) allow it to participate in a wide variety of geochemical and biogeochemical processes. Depending on its redox state and controlling species, sulfur dissolved in magma may be fractionated into a water-rich phase and sulfur-bearing minerals. Retrieving information on the original sulfur abundance and isotopic signature of a magma is challenging and requires deciphering the different processes that may have operated during its evolution en route to the surface. Advances made in thermodynamic modeling, experimentation on sulfur solubility and diffusion in silicate melts, and microanalytical techniques for probing sulfur’s speciation and isotopic signature at the micrometer scale are providing an outstanding picture of sulfur evolution in magmas.