Frontiers in Textural and Microgeochemical Analysis
Dougal A. Jerram and Jon P. Davidson – Guest Editors
Table of Contents
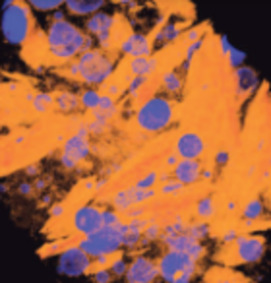
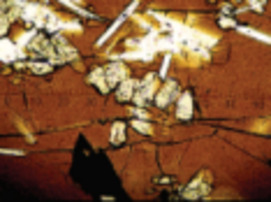
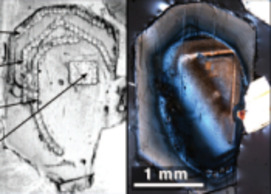
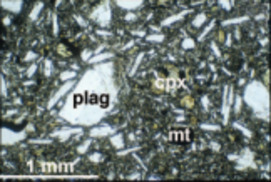
Recent advances have been made in high-resolution in situ methods to image mineral growth pat- terns, analyse compositional and isotopic zonation, and improve our ability to visualize, study, and model rock textures in three dimensions. These advances pro- vide a significant step forward in the understanding of how rocks form and the history they can tell us. Computer-aided reconstructions and 3D modelling of textures, advanced models of crystallisation and very high-resolution sampling of within-crystal geochemical variations are at the frontiers of current studies in igneous petrology. This thematic issue will highlight the integration of textural and geochemical information as a powerful tool in the understanding of igneous rocks, and will provide examples that researchers in other disciplines may use to further advance their studies.
Frontiers in Textural and Microgeochemical Analysis
3D Analysis of Rock Textures: Quantifying Igneous Microstructures
Igneous Textures: On the Kinetics behind the Words
Isotopic Microsampling of Magmatic Rocks
- Crystal Zoning as an Archive for Magma Evolution
- Measuring Timescales of Magmatic Evolution
Australian Scientific Instruments (ASI)
Cambridge University Press
CAMECA
CrystalMaker Software
Excalibur Mineral Corporation
Geological Society of London
Hudson Institute of Mineralogy
JKTech Pty Ltd
Materials Data (MDI)
Meiji Techno America
New Wave Research
PANalytical
Rigaku
RockWare
Thermo Fisher Scientific
v3n5 Critical Zone: Where Rock Meets Life
Guest editor: Susan L. Brantley (Penn State), Timothy S. White, and K. Vala Ragnarsdottir
The Critical Zone (CZ) encompasses all fluid, mineral, gaseous, and biotic components from the outer envelope of vegetation down to the lower limit of groundwater. It supports much of life on Earth. Important, relevant societal challenges related to CZ science to be addressed in the next decade are: (1) what processes control fluxes of carbon, particulates, and other reactive gases into and from the CZ? (2) how do weathering processes in the CZ nourish ecosystems? (3) how do chemical and physical weathering processes shape the CZ? and (4) how do biogeochemical processes in the CZ govern long-term sustainability of water and soil resources?
Crossing Disciplines and Scales to Understand the Critical Zone Susan L. Brantley (Penn State), Martin B. Goldhaber, and K. Vala Ragnarsdottir
Physical and Chemical Controls on the Critical Zone Suzanne Prestrud Anderson, Friedhelm von Blanckenburg (GFZ Potsdam), and Arthur F. White
Soil Biogeochemical Processes within the Critical Zone Jon Chorover (University of Arizona), Ruben Kretzschmar (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology), Ferran Garcia-Pichel, and Donald L. Sparks
Coupling between Biota and Earth Materials in the Critical Zone Ronald Amundson (University of California, Berkeley), Daniel D. Richter (Duke University), Geoff S. Humphreys (Macquarie University), Esteban G. Jobbágy, and Jérôme Gaillardet (IPG, Paris)
Contributions from Earth’s Atmosphere to Soil Louis A. Derry and Oliver A. Chadwick
- Zircon – Tiny but Timely (February 2007)
- On the Cutting Edge: Teaching Mineralogy, Petrology, and Geochemistry (April 2007)
- Energy: A Geoscience Perspective (June 2007)
- Frontiers in Textural and Microgeochemical Analysis (August 2007)
- Critical Zone: Where Rock Meet Life (October 2007)
- Medical Mineralogy and Geochemistry (December 2007)
Download 2007 Thematic Preview